Lvwo Technology collects cards all day long, providing a higher than the market competitiveness exchange rate and a reliable cooperation platform. Welcome all card merchants to negotiate and cooperate。
Keyword: moneylion 5104, stable 5392, business card 555740, 5396 onebank , 4985 chime, 4115 current , 4358netspend, 41088 Karma ....
Please identify official WeChat: lvwocfo only this wechat, the others are counterfeit, be careful to choose!
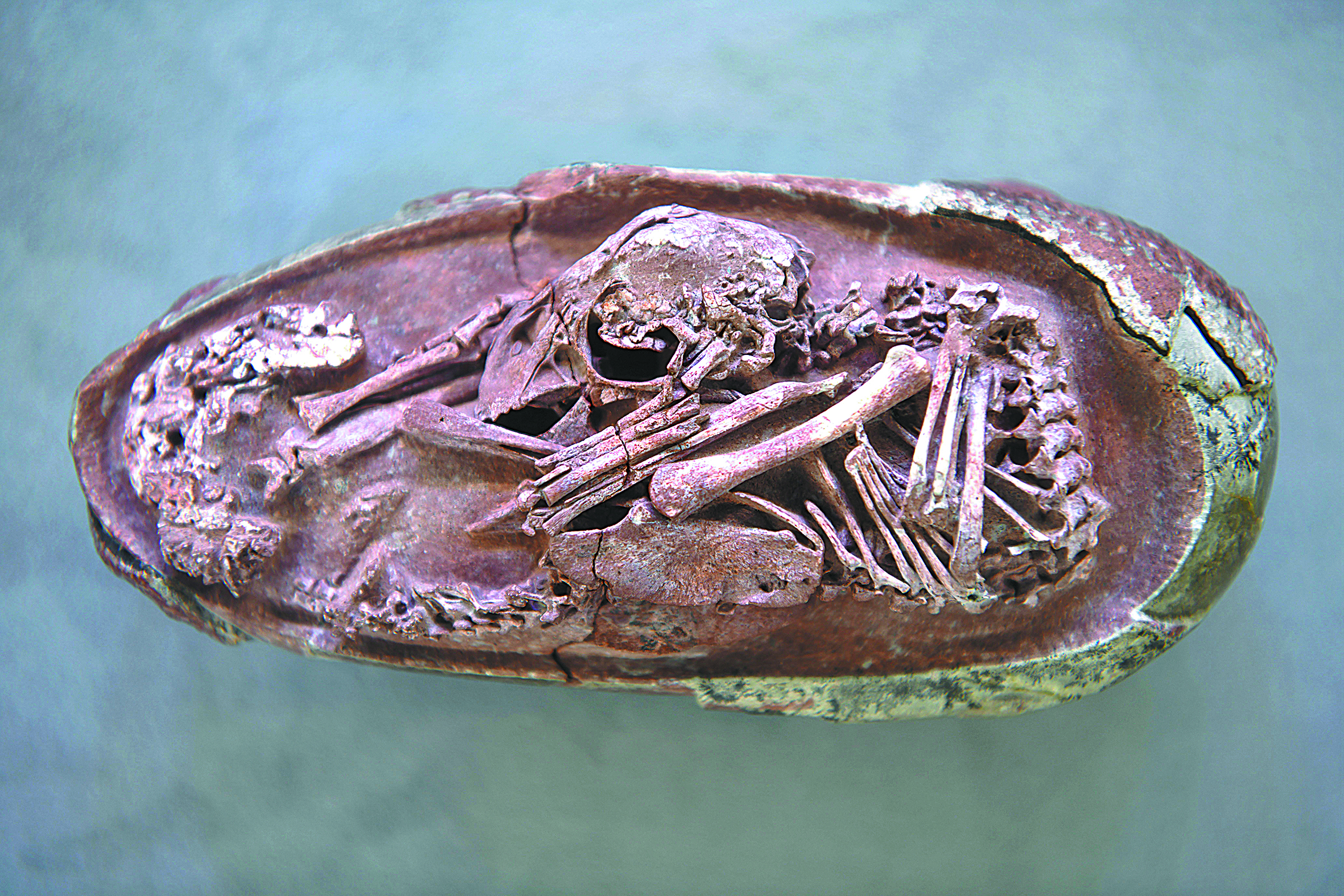
A new study examining an embryo from a fossilized dinosaur egg has provided further evidence supporting the notion that modern birds evolved from dinosaurs.
The embryo fossil was discovered in rocks in Ganzhou, Jiangxi province, around the year 2000 and is housed in the Yingliang Stone Nature History Museum in Fujian province, where it was dubbed "Baby Yingliang".
Estimated to be 27 centimeters from head to tail, the creature lies inside a 17-cm-long egg. Paleontologists believe it belongs to a toothless theropod dinosaur, or oviraptorosaur, dating back 72 to 66 million years, within the Cretaceous Period.
The posture of the embryo within the egg implies that these dinosaurs developed birdlike postures close to hatching, according to the study published in the journal iScience on Wednesday.
Scientists from China, Britain and Canada who worked on the study found the posture of "Baby Yingliang" unique among known dinosaur embryos-its head lies below the body, with the feet on either side and the back curled along the blunt end of the egg. Previously unrecognized in dinosaurs, this posture is similar to that of modern bird embryos.
Before hatching, birds are known to develop a series of tucking postures, bending their body and extending their head under their wings. Embryos that fail to attain such postures have a higher chance of death due to unsuccessful hatching.

 大熊 之家绿沃科技
大熊 之家绿沃科技